lv pv loop | pv loop during exercise lv pv loop To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. When this is done, a PV loop is generated (bottom panel of figure and linked YouTube video). Lvl: 40 Sea Stealh Attack Farm - credit: bmsmota. Restart. 20 cards. Build in Deck Builder. Strategy. Use Restart to have a better chance of having A Legendary Ocean / Warrior of Atlantis and a monster to summon. Keep attacking Yugi Muto face-down monsters so they can't flip summon.
0 · why study pv loops
1 · right ventricular pressure volume loop
2 · pv loops heart
3 · pv loop during exercise
4 · pv loop catheter
5 · pv loop afterload
6 · normal pv loop
7 · importance of pv loops
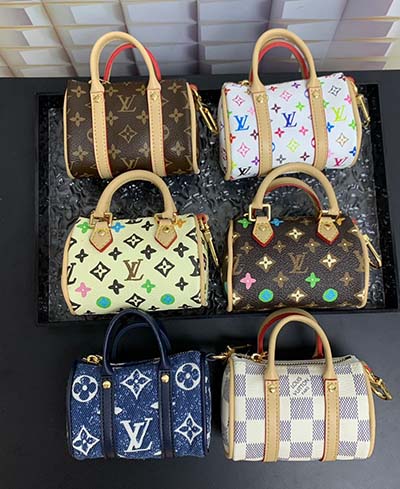
Cheap Louis Vuitton bags from China or Amazon Louis Vuitton dupes are far less likely to incorporate all the tiny details, including: Legit LV labels; Date code; Quality stitching; Quality hardware (e.g., zippers, buckles) .
To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against .To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. When this is done, a PV loop is generated (bottom panel of figure and linked YouTube video).
why study pv loops
A PV loop plots the changes in ventricular pressure associated with the changes in volume which occur during the cardiac cycle. The plot of a ventricular pressure-volume loop contains the following information: Volumes: End-diastolic volume (where the mitral valve closes) End-systolic volume (where the aortic valve closes)
Real-time left ventricular (LV) pressure–volume loops provide a framework for understanding cardiac mechanics in experimental animals and humans. Such loops can be generated by real-time measurement of pressure and volume within the left ventricle.
Left ventricular pressure-volume relationship and ECG waveforms during systole and diastole. When left ventricular pressure exceeds diastolic pressure in the aorta, the aortic valve opens and blood is ejected into the aorta. PV loops from these healthy individuals displayed the classic domed shape and illustrate how RV end-systolic pressure decays nearly to end-diastolic pressure during exercise and, unlike LV physiology, that ejection proceeds well past end-systole. In PV loop diagrams, increased inotropy increases the slope of the end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (ESPVR; upper dashed lines in figure), which permits the ventricle to generate more pressure at a given LV volume. Decreasing inotropy has the opposite effects; namely, increased end-systolic volume and decreased stroke volume and . Please draw and describe the pressure volume loop of the left ventricle. Examinee response: Drawing and explanation in real-time video/audio. Examiner Explanation. Transcript. This pressure volume loop diagram represents the 5 phases of the cardiac cycle.
Pressure-volume loops are graphs showing the changing relationship between left ventricular pressure and volume during a cardiac cycle. They provide useful information such as stroke volume or end-diastolic volume, as well as systolic, diastolic, and pulse pressure. Advanced Pressure Volume Loops. The easiest way to approach more complicated pressure-volume loops is to address each of the basic factors before trying to draw the curve: How is preload changed? How is afterload changed? How is contractility changed? How are isovolumetric contraction and isovolumetric relaxation changed?The PV loops provide immediate insights into the effects of mitral interventions such as edge-to-edge mitral repair. Changing PV loop morphology can help tailor positioning and/or determine number of clips to optimize a final result and help differentiate responders from non-responders.To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. When this is done, a PV loop is generated (bottom panel of figure and linked YouTube video).
A PV loop plots the changes in ventricular pressure associated with the changes in volume which occur during the cardiac cycle. The plot of a ventricular pressure-volume loop contains the following information: Volumes: End-diastolic volume (where the mitral valve closes) End-systolic volume (where the aortic valve closes)
Real-time left ventricular (LV) pressure–volume loops provide a framework for understanding cardiac mechanics in experimental animals and humans. Such loops can be generated by real-time measurement of pressure and volume within the left ventricle.Left ventricular pressure-volume relationship and ECG waveforms during systole and diastole. When left ventricular pressure exceeds diastolic pressure in the aorta, the aortic valve opens and blood is ejected into the aorta. PV loops from these healthy individuals displayed the classic domed shape and illustrate how RV end-systolic pressure decays nearly to end-diastolic pressure during exercise and, unlike LV physiology, that ejection proceeds well past end-systole.
In PV loop diagrams, increased inotropy increases the slope of the end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (ESPVR; upper dashed lines in figure), which permits the ventricle to generate more pressure at a given LV volume. Decreasing inotropy has the opposite effects; namely, increased end-systolic volume and decreased stroke volume and .
Please draw and describe the pressure volume loop of the left ventricle. Examinee response: Drawing and explanation in real-time video/audio. Examiner Explanation. Transcript. This pressure volume loop diagram represents the 5 phases of the cardiac cycle.Pressure-volume loops are graphs showing the changing relationship between left ventricular pressure and volume during a cardiac cycle. They provide useful information such as stroke volume or end-diastolic volume, as well as systolic, diastolic, and pulse pressure. Advanced Pressure Volume Loops. The easiest way to approach more complicated pressure-volume loops is to address each of the basic factors before trying to draw the curve: How is preload changed? How is afterload changed? How is contractility changed? How are isovolumetric contraction and isovolumetric relaxation changed?
right ventricular pressure volume loop
pv loops heart
Step into the Venetian-inspired lobby at Las Vegas's Venetian Hotel. Marvel at intricate Italian architecture, opulent décor, and the grandeur of Venetian ae.
lv pv loop|pv loop during exercise